Target systems: Active Directory, LDAPS, Radius
Good to know: Active Directory, LDAPS and Radius are authentication infrastructures that are used for the utilisation of identities (persons) and for the assignment of access rights in a network. They ensure that only authenticated users (persons) can access information and systems.
Identity and Access Management
ETH Zurich operates an Identity and Access Management (IAM) system, known to us as the ETH Web Center. The system enables the control and supply of data to the directory services (Active Directory, LDAP and Radius). This makes it possible to create user accounts, and it standardises the management of groups and distributors.
Image ETH Web Center
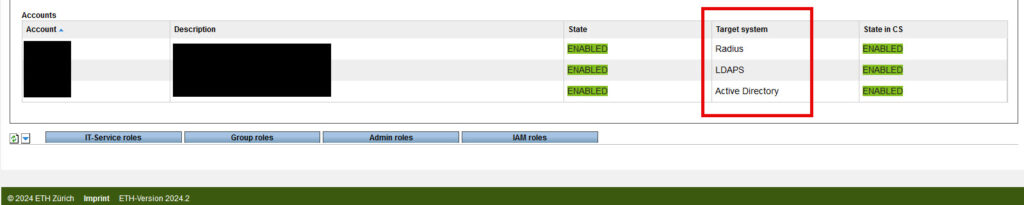
ETH Web Center Tab Self Service > User overview > Section Accounts
Target systems
The term «target systems» refers to the specific platforms or services within an IT infrastructure. At ETH, the target systems are used for authentication and, in some cases, also for authorisation. They ensure that the people who log in are genuine. In a practical context, a target system can be anything from a server to a database to an application programme.
Active Directory
The Active Directory (AD) is a directory service developed by Microsoft that is used in application resources. It enables the management of user accounts and computer objects (IT devices). Administrators can use it to control resources, manage user rights and enforce policies. The most common applications that are offered as an Active Directory service by IT Services (SLA) for ETH members are:
- When logging in on your personal computer (desktop/laptop)
- Exchange (Outlook, email)
- SharePoint
- Confluence
- Teams
- OneDrive
- Zoom
- Almost all cloud services
LDAPS
LDAPS stands for «Lightweight Directory Access Protocol Secure» and is a protocol that is used to retrieve and change information from directory services (such as user names and passwords). Like AD, the LDAPS service is an ETH-wide authentication, authorisation and information service. LDAPS service is based on the OpenLDAP software. It serves as a central source of information for applications and systems and enables the exchange of information about users, groups, systems and services (SLA).
Radius
Radius (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) is a network protocol that is used for the authentication, authorisation and accounting (AAA) of users. It is used to manage access control to networks, especially wireless networks and Internet access services. RADIUS is used for the VPN network access service.
Conclusion
AD, LDAPS and Radius have an SSL layer (Secure Sockets Layer) to encrypt communication between the client and the servers and thus increase data security.
Image of Web Center
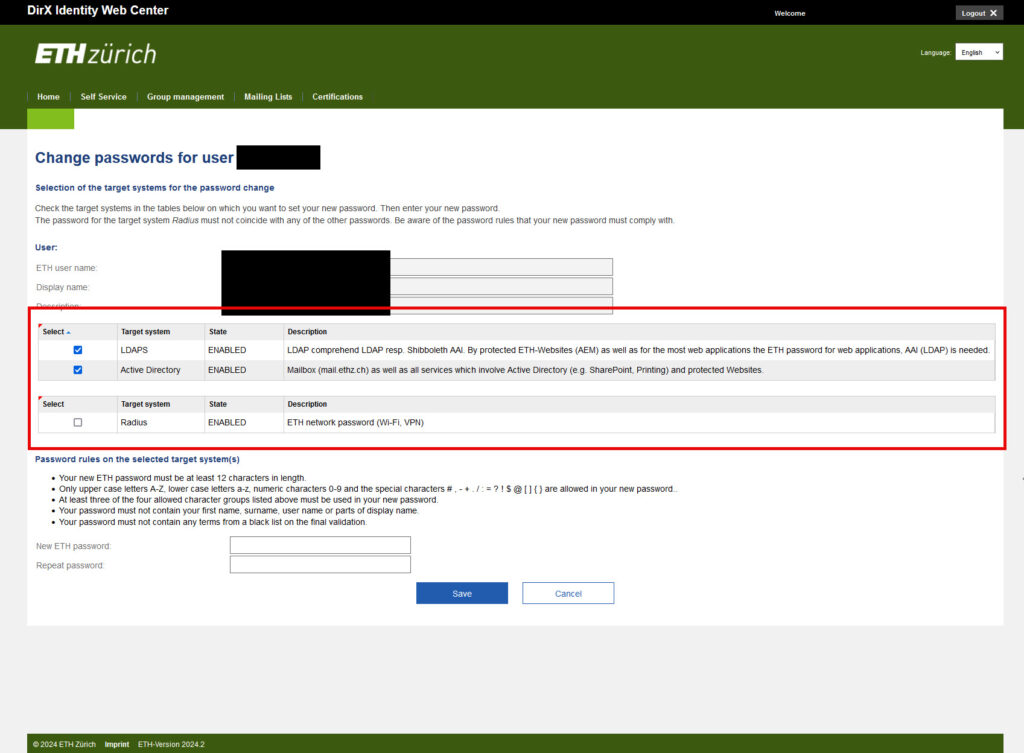
ETH Web Center Tab Self Service > Change password > Change passwords for user «XXX» > Selection of the target systems for the password change
Identity & Access
An «ETH user account» (IT Knowledge Base) is created for each ETH member when they join the university. This account contains a variety of service roles (services such as mailbox, VPN, etc.) as well as identities in various target systems (Active Directory, LDAP, Radius). In the Web Center you can see in which target systems an account exists and manage your passwords.
There are three different ETH passwords
- ETH password for web applications, AAI (LDAP)
- ETH password for email (Active Directory)
- ETH network password (Radius)
And two password groups
- Group = The ETH password for web applications, AAI (LDAP) and the ETH password for email (Active Directory)
- Group = ETH network password (Radius)
The password for the Radius target system must be different from the password for web applications, AAI (LDAPS) or email (Active Directory).


